DFG:User Authority Maintenance
User Authority Maintenance
The User Authority Maintenance function enables you to maintain the functional security for the application you are working with by grouping users into a pre-defined TD/OMS authorization class.
Users who are not authorized to start a specific function receive a message on their display.
In addition to functional security, specific rights can be assigned to users per environment (See Environment Maintenance).
A user belonging to the group *SECOFR, *SECADM, and the TD/OMS manager can start this function.
Code 3 users are also allowed to start this function once they have been declared.
The TD manager and the users belonging to the *SECOFR and *SECADM class are not automatically granted application rights for other functions.
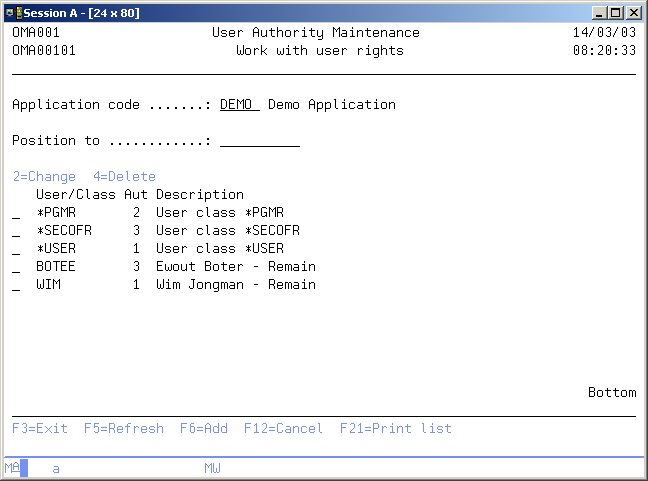
Work with User Rights
The Work with User Rights display shows the currently authorized users, user groups, and/or user classes for the current application with their assigned authorization code. You can add an entry to the list, remove an entry from the list, or change the entry's assigned authorization code.
Active Application
The active application shows the code of the currently active application. If this field can be changed, you can activate a new application by typing the application you desire and pressing Enter. You can also use the F4=Prompt key to select an application from the list of available applications.
Position to
Use this prompt to go to a particular application in the list.
Option
Use this column to perform different operations on individual entries. The possible values are:
- 2=Change
Change the authorization code of a user, user group, or class. - 4=Delete
Delete the entry from the list. - F21=Print list
Print a user list to your job's current active output queue.
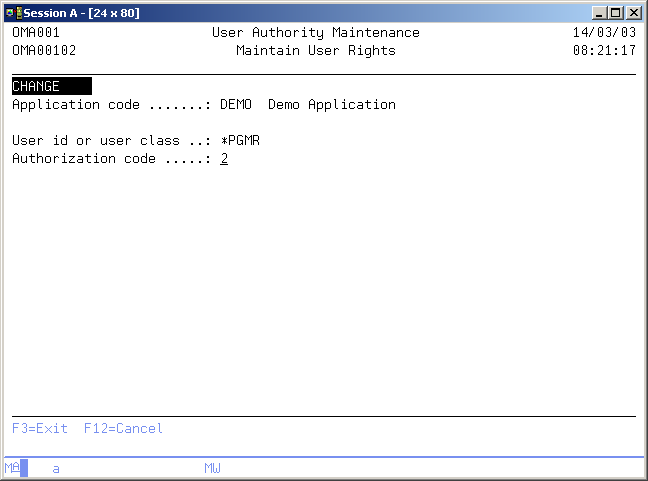
Maintain User Rights
The Maintain User Rights display shows information and enables actions depending on the option chosen on the previous display. The chosen action on the previous display is shown on line three. The following actions can be activated;
- Add
You can add a new entry definition. The entry code and the assigned authorization code must be entered. - Change
You can change the assigned authorization code of an existing entry definition. The current authorization code will be shown. The authorization code can be changed at any time. - Delete
The current entry and authorization code will be shown, including a confirmation message.
User ID or User Class
The user ID or user class element contains an OS/400 user, user group, or user class. The following rules apply to each entry:
- User ID
Enter a valid name of an existing user profile. This is the most detailed level to assign an authorization code to and will overrule any other definition. - User group
Enter a valid name of an existing user group profile. All members of this group are implicitly selected. Specifications at the user level, however, overrule the specifications per user group. - User Class
Enter A Valid User Class. All users belonging to a specified class are implicitly selected. Specifications at group and user level, however, overrule the specification per class.
Use F4=List to get a list of the available users.
Authorization code
TD authorization code determines which TD/OMS functions can be executed for a user, user class, or user group. Some TD/OMS functions also require authority at the environment level. Valid authorization codes are:
- 0=None
No rights are assigned to the related users. This value is useful if authorization codes are assigned at the group or class level and one user has to be omitted. - 1=User
Only functions at the end-user level can be executed. In general, these users can maintain their own user requests and inquire about the related Fix information. The request processor can maintain the requests from all users if this user is assigned authorization code 1. - 2=Programmer
Code two is specially meant for functions at programmer level. They are allowed to maintain their own fixes, connect objects to fixes, and start Fix Processing. Specific authorization depends on the rights assigned at the environment level. The request processor can maintain the fixes from all programmers if this user is assigned authorization code 2. - 3=Application manager
Users with code 3 are application managers and have rights for all functions at the application level.
The assigned authorization code can be changed at any time.
Command Start User Authority Maintenance (STRUAM)
This menu command starts the user authority maintenance function. Refer to the description of the function User Authority Maintenance for a detailed description.
This command has no parameters.
Application level authorization rules
Authorization to an application is determined based on the following sequence. As soon as a valid authorization is found at any level, that authorization is applied. And no further checks will be performed:
- User level Authorization
- If the user has direct authorization to the application, that will be used.
- Group level Authorization
- If the user does not have direct authorization, the system checks for authorization at the group level. This includes both the user’s primary group and any supplemental groups. The group with the highest level of authorization will be considered.
- User class level Authorization
- If the user class has direct authorization to the application, that will be used.
- Group class level Authorization
- The system checks for authorization at the group class level. This includes the user’s group class and the classes of supplemental groups. The group class with the highest level of authorization will be considered.
Environment level authorization rules
If environment level authority is defined for a user, user group, or user class, all authorized users must be explicitly listed. The Authorization to an environment is determined based on the following sequence. As soon as a valid authorization is found at any level, that authorization will be applied and no further checks will be performed:
- Environment level authorization is not marked.
- When no environment-specific authority is defined, Code 2 is allowed for all environments except Production, and Code 3 is allowed for all environments.
- User level Authorization
- If the user has direct authorization to the environment, that will be used.
- Group level Authorization
- If the user does not have direct authorization to environment, the system checks for authorization at the group level. This includes both the user’s primary group and any supplemental groups. The group with the highest level of authorization will be considered.
- User class level Authorization
- If the user class has direct authorization to the environment, that will be used.
- Group class level Authorization
- The system checks for authorization at the group class level. This includes the user’s group class and the classes of supplemental groups. The group class with the highest level of authorization will be considered.