DFG:Application Definition
Application Definition
The Application Definition function enables you to maintain the initial application definition. The application code must be known to TD/OMS before any function can be executed for a specific application.
Application definitions can be added, changed, deleted or copied from another application. The definition contains parameters at application level.
Users belonging to the group *SECOFR or *SECADM, and the TD/OMS manager are allowed to start this function.
Note: The function User Authority Maintenance must be executed once to declare the authorized users for that specific application, after entering an initial definition for an application.
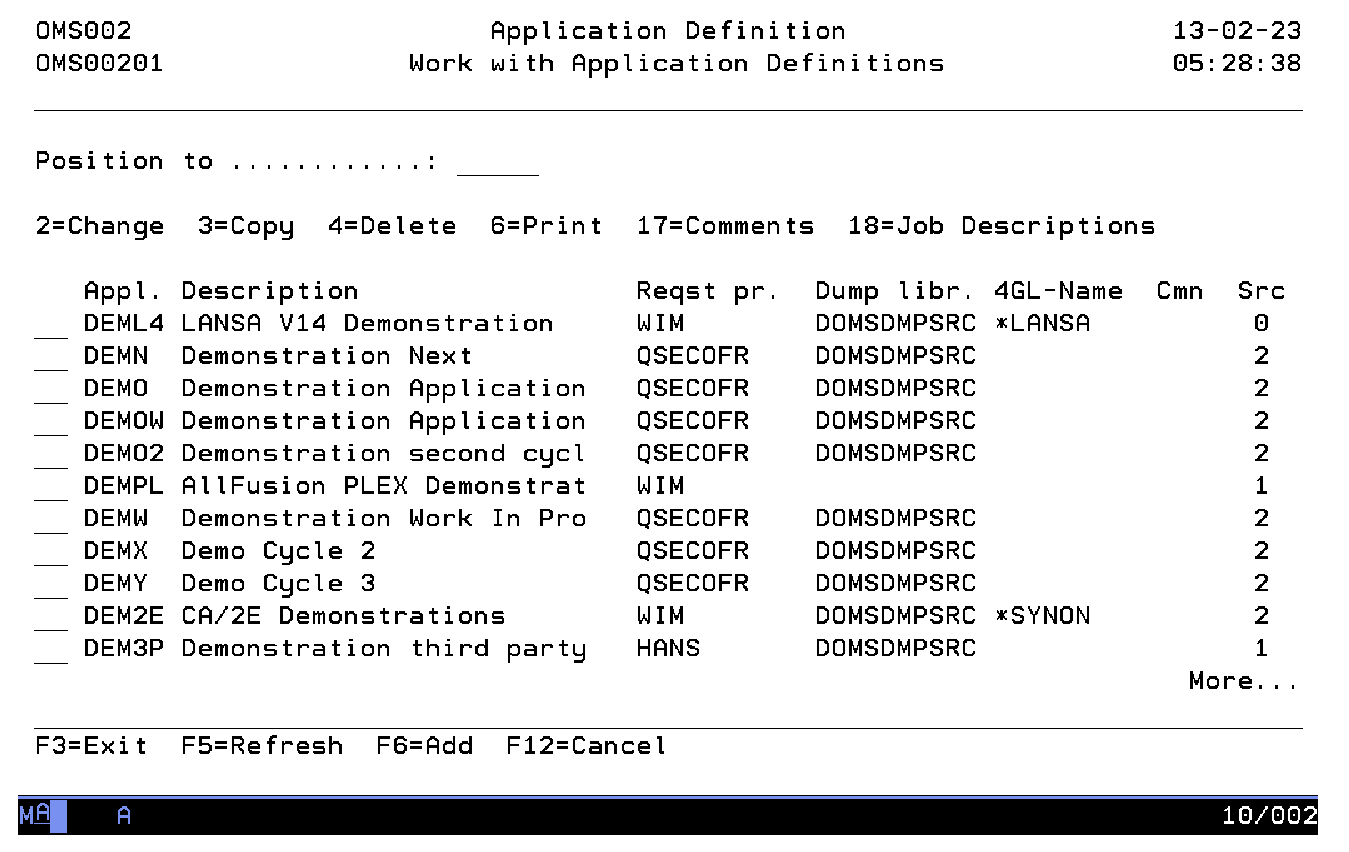
Work with Application Definitions
The Work with Application Definitions display shows the currently defined applications, including their main parameters. To select an option, type the option number in the option field area and press Enter. For more information about an option move the cursor to the option column and press Help. For more information about a function key, move the cursor to the function key area and press Help.
Position to
Use this prompt to go to a particular application in the list.
Option
Use this column to perform different operations on individual entries. Type the option number next to an entry and press Enter.
- 2=Change
Change the contents or certain attributes of an application.
- 3=Copy
Add a new application definition and at the same time copy one or more parts of the extended definition of an existing application.
- 4=Delete
Delete the definition of an application.
- 6=Print
Print the application definition.
- 17=Comments
Work with the comments and replies associated with the application.
- 18=Job Descriptions
Work with the job descriptions.
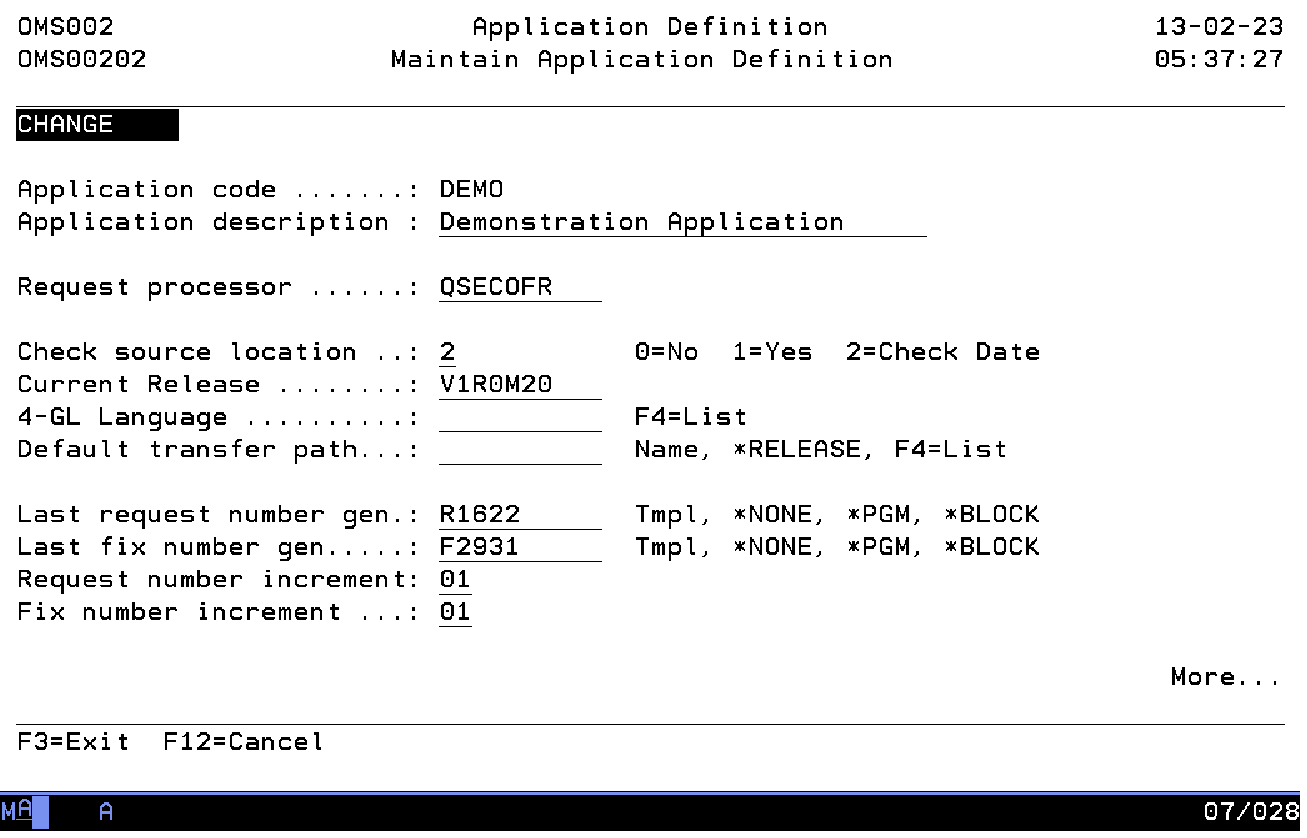
Maintain Application Definition
The Maintain Application Definition display shows information and allows actions depending on the option chosen on the previous display. The chosen action on the previous display is shown on line three. The following modes can be activated:
- Add
You can add a new application definition. The application code and all attributes must be entered.
- Change
You can change the attributes of an existing application definition. The current values are shown. All attributes can be changed at any time during the life cycle of an application.
- Delete
The current contents of all attributes is shown including a confirmation message. Deletion of application definitions is only allowed if no related information is stored in the TD database.
Note: For more information about a specific attribute move the cursor to the attribute area and press Help.
Application code
The application code is a unique identification of the application. Once the code has been added it cannot be changed. To change the application code you have to delete the old application code and add a new one. A blank value is not allowed. Almost all data defined in TD/OMS is related to an application. In general an application groups information about:
- Security
Security Rights and privileges assigned to users for a specific application.
- Environment
The definition of phases in the maintenance cycle for a specific application.
- Objects
The definition of objects pertaining to a specific application.
- Requests
The history of user requests concerning the specific application.
- Fixes
The description of a unit of work, both completed and in process.
- Exceptions
The definition of exception functions and exception selections.
Application description
The application description contains a description of the application code. A blank value is not allowed.
Request processor
The request processor is one of the persons who is in charge of the request handling and who will receive an informational message if another user has entered a new request. He is allowed to maintain all requests and fixes belonging to this application. The name of the request processor is mandatory and must be known to OS/400 as a user profile object.
Note: that the request processor must also have an authorization code assigned to him in order to enable him to work with requests and/or fixes.
Check source location
The Check source location indicator instructs TD/OMS how to handle source members related to an object. The possible values are:
- 0=No
The value "0" indicates that in general the objects do not have a related source in this particular system. No errors will occur if no source can be found if a new object is registered in the TD database. Use this value for instance for applications in remote systems where no sources reside, or if you wish to register some objects from the QSYS library.
- 1=Yes
The value "1" indicates that objects do have related sources in this system. The environment definition determines the way TD/OMS searches for the right source member. Information about source change date of object and source is stored in TD, but a mis-match does not cause an error.
- 2=Check Date
The value "2" is equal to value "1". Mis-match of source change date between object and source will result in an error. This value is recommended if objects have sources in this system.
Release
A release identification can be used to bundle fixes and will commonly be formatted as VnRnMnn, where V stands for Version, R for Release and M for Modification level. Any other format is allowed, including a blank value. The current release indicates the default value for release whenever a new fix is added.
Another way of working with releases can be achieved by defining each release as an application. Refer to the concepts guide for more detailed information.
4GL name
The 4GL name can be defined in Application Definition, indicating that the specified 4GL or Case tool is used, possibly in combination with 3GL compilers. Defining a 4GL name will enable you, in general, to register 4GL objects in TD/OMS and handle them like OS/400 objects. Specific information about the functions per 4GL / Case tool are described in the relevant interface manual.
You will also need to specify 4GL logical library names in the 4GL Library Definition function in order to work with the 4GL objects.
Use F4=List to get a list of the available 4GL interfaces.
Note: You will need the TD interface module in order to work with the 4GL objects.
Default Transfer Path
A default transfer path indicates the default value for the transfer path whenever a new fix is added.
Use F4=List to get a list of the available transfer paths. When the list is empty, you can use STREM (Environment Maintenance) to add transfer paths to your environment.
The special value *RELEASE applies to the value given in the previously mentioned Release. When you are using the value *RELEASE you need to be sure that there is a transfer path defined with the same name as the release.
Last request number
The last request number is used by TD/OMS as a base for generating request numbers. TD/OMS will generate the request number if the default request number "*GEN" has been used during the addition of a Request. The generated Request number is stored in this attribute. The last Request number is shown and can be maintained in the Application Definition function.
The following rules apply to generation of numbers:
- If the string ends with an alphabetic character TD/OMS will extend the string with "0000".
- If the string ends with a numeric character TD/OMS will use all ending numeric characters as a base.
Examples: (Assume increment value is 1)
Base Value Generated value R R0001 R1 R2 R9 R10 ABCDEFGHI ABCDEF0001 R00000000 R00000001
Last fix number
The Last fix number is used by TD/OMS as a base for generating fix numbers. During addition of a fix, TD/OMS will generate the fix number if the default fix number "*GEN" has been used. The generated fix number is stored in this attribute. The Last fix number is shown and can be maintained in the Application Definition function.
The following rules apply to generation of numbers:
- If the string ends with an alphabetic character TD/OMS will extend the string with "0000".
- If the string ends with a numeric character TD/OMS will use all ending numeric characters as a base.
Examples: (Assume increment value is 1)
Base Value Generated value F F0001 F1 F2 F9 F10 ABCDEFGHI ABCDEF0001 F00000000 F00000001
Request number increment
The request number increment value is used by TD/OMS for generating request numbers. Before generating a request number the "Last request number gen." is incremented with this value. This value is shown and can be maintained in the Application Definition function.
Fix number increment
The fix number increment value is used by TD/OMS for generating fix numbers. The "Last fix number gen." is incremented with this value before generating a fix number. The value is shown and can be maintained in the Application Definition function.
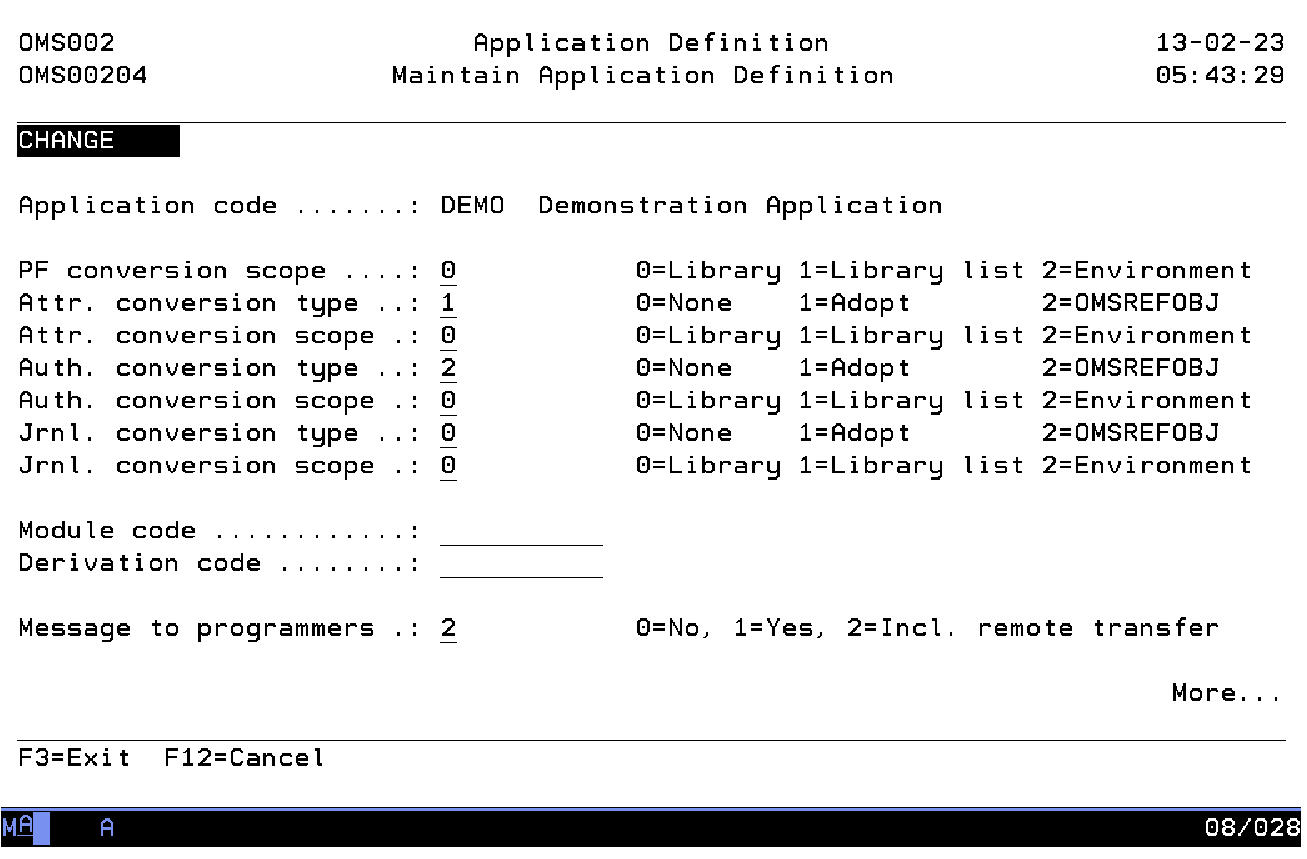
Data conversion scope
The data conversion scope is used to indicate where to search for a reference object if the data of a physical file has to be converted during Object Transfer. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=Library
The data is only converted if the reference object exists in the library where the new object has to be created.
- 1=Library list
The data is only converted if the reference object exists in the library list where the new object has to be created. The libraries are searched in order of definition.
Note: The library list mentioned here is the TD library list as defined in the environment definitions.
- 2=Environment
The data is only converted if the reference object exists in the environment where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Attribute conversion type
The attribute conversion type instructs Object Transfer what to do with the object attributes of an OS/400 object. Copying of the object attributes is only applicable for OS/400 objects with a prompt override program specified in the CHG.... command. The possible values are:
- 0=None
No additional copying of attributes is done, except for logical files, because objects are by default copied and thus the object attributes will also be copied.
The object attributes of the logical file in the source environment are copied to the newly created logical after compilation. This is because logicals are compiled instead of duplicated.
If the object is created by an exception at user exit point 5 the exception must also copy the object attributes.
- 1=Adopt
The attributes are copied from a reference object with same object code and object type in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the attribute conversion scope. The reference object 'OMSREFOBJ' will be used as if value '2' has been used if no equally named reference object can be found.
- 2=OMSREFOBJ
The attributes are copied from a reference object 'OMSREFOBJ' with same object type in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the attribute conversion scope.
No further processing is done for the attributes if object OMSREFOBJ cannot be found.
Attribute conversion scope
The attribute conversion scope is used to indicate where to search for a reference object if the attributes of an OS/400 object have to be changed during Object Transfer. The possible values are:
- 0=Library
The object attributes are only copied if the reference object exists in the library where the new object has to be created.
- 1=Library list
Attributes are copied if the reference object exists in the library list where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Note: The library list mentioned here is the TD library list as defined in the environment definitions.
- 2=Environment
Attributes are copied if the reference object exists in the environment where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Authority conversion type
The authority conversion type instructs Object Transfer what to do with the object owner and authority of an OS/400 object. Copying of the object owner and authorities is only applicable for OS/400 objects. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=None
No additional copying of authority is done.
- 1=Adopt
The owner and authorities are copied from a reference object with same object code and object type in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the authority conversion scope.
The reference object 'OMSREFOBJ' will be used if no equally named object can be found. This is the same as code '2'.
- 2=OMSREFOBJ
The owner and authorities are copied from a reference object 'OMSREFOBJ' with type *DTAARA in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the authority conversion scope.
This data area 'OMSREFOBJ' can be created with TYPE(*CHAR) and LEN(1) and without contents.
No further processing is done for ownership and authorities if data area OMSREFOBJ cannot be found.
Authority conversion scope
The authority conversion scope is used to indicate where to search for a reference object if the owner and authorities of an OS/400 object has to be changed during Object Transfer. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=Library
The authority is only copied if the reference object exists in the library where the new object has to be created.
- 1=Library list
The authority is copied if the reference object exists in the library list where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Note: The library list mentioned here is the TD library list as defined in the environment definitions.
- 2=Environment
The authority is copied if the reference object exists in the environment where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Journal conversion type
The journal conversion type instructs Object Transfer what to do about journaling of an OS/400 physical file. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=None
Physical files will not be journalled automatically.
- 1=Adopt
The physical file will be journalled in the same way as a reference physical file in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the journal conversion scope.
A reference physical file 'OMSREFOBJ' will be used if no equally named reference object can be found as if value '2' has been used.
- 2=OMSREFOBJ
The physical file will be journalled in the same way as a reference physical file with the name 'OMSREFOBJ' in the target library, target library list or target environment, depending on the journal conversion scope.
The physical file will not be journalled automatically if no 'OMSREFOBJ' object can be found.
Journal conversion scope
The journal conversion scope is used to indicate where to search for a reference object if a physical file has to be checked for journalling during Object Transfer. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=Library
Journalling of the physical file is only done if the reference object exists in the library where the new object has to be created.
- 1=Library list
Journalling of the physical file is done if the reference object exists in the library list where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Note: The library list mentioned here is the TD library list as defined in the environment definitions.if the reference object.
- 2=Environment
Journalling of the physical file is done if the reference object exists in the environment where the new object has to be created. The library lists are searched in order of definition.
Module code
The module code is not applicable at this time.
Derivation code
The derivation code is not applicable at this time.
Message to programmer
The message to programmer specifies if a programmer has to be informed if a fix, which has been assigned to her/him, is changed by another user. The default value is '0'. The possible values are:
- 0=No
No messages will be sent to the programmer.
- 1=Yes
The programmer will receive a message if another user adds a new Fix with his name specified as programmer, or if another user starts Object Transfer for a Fix, with his or her name specified, to or from the development environment.
- 2=Incl. remote transfer
The programmer will additionally receive a message when a transfer to production is performed on a remote system.
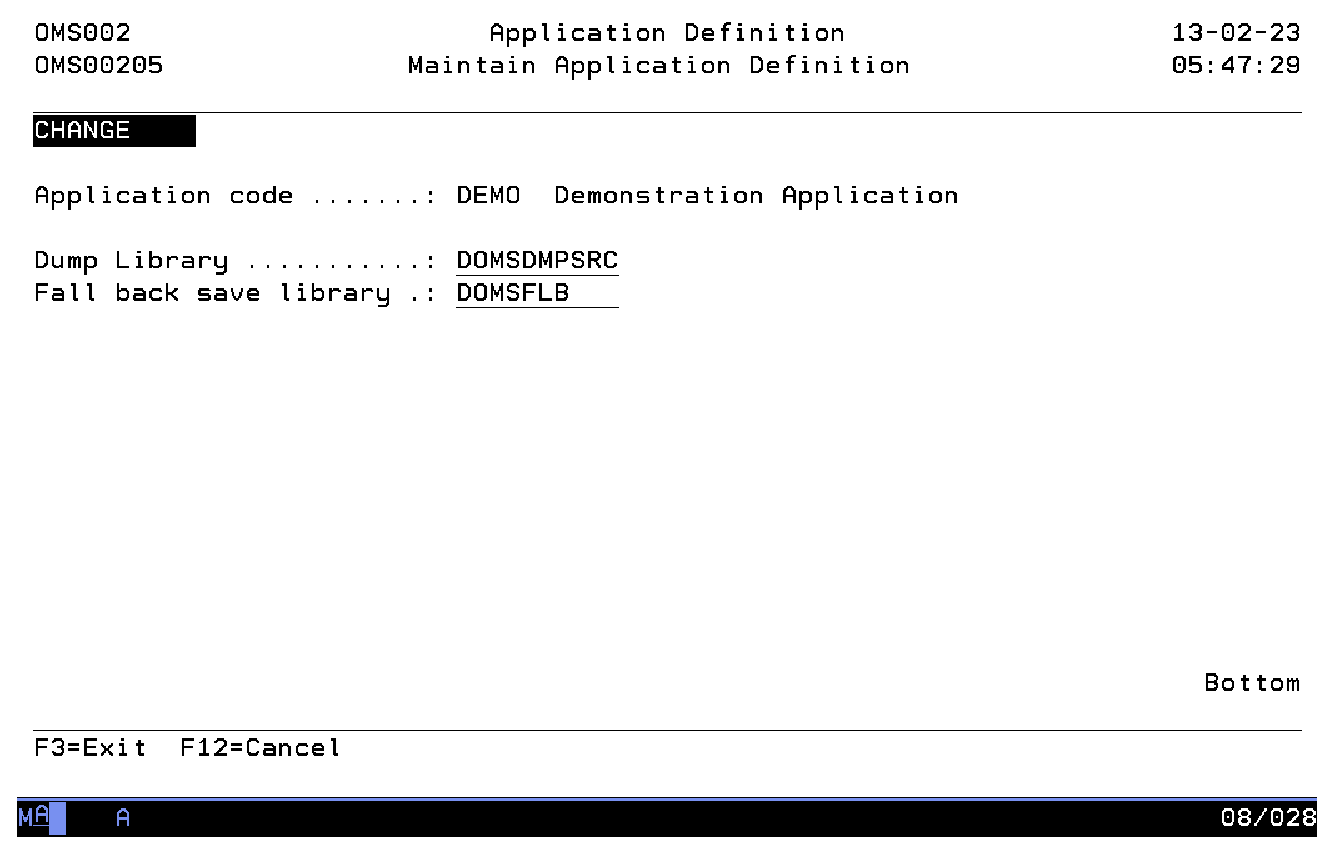
Dump library
The source archive library is a valid OS/400 library name in which TD/OMS saves the old source if an object or source member is moved or copied from the production environment. Old sources will not be saved if the name of this library is blank. The necessary source files are automatically created by TD/OMS and a unique member name is generated. The saved information is logged and can be accessed by using the Dumped Sources Maintenance function.
Fall back save library
The fall back save library is a valid OS/400 library name and is defined in the Application definition function. Leave this field blank if you do not wish to use fall back options.
If a valid library name is entered TD/OMS will use this library to store the savefiles with the replaced objects. The library list definitions determine if replaced objects are to be saved.
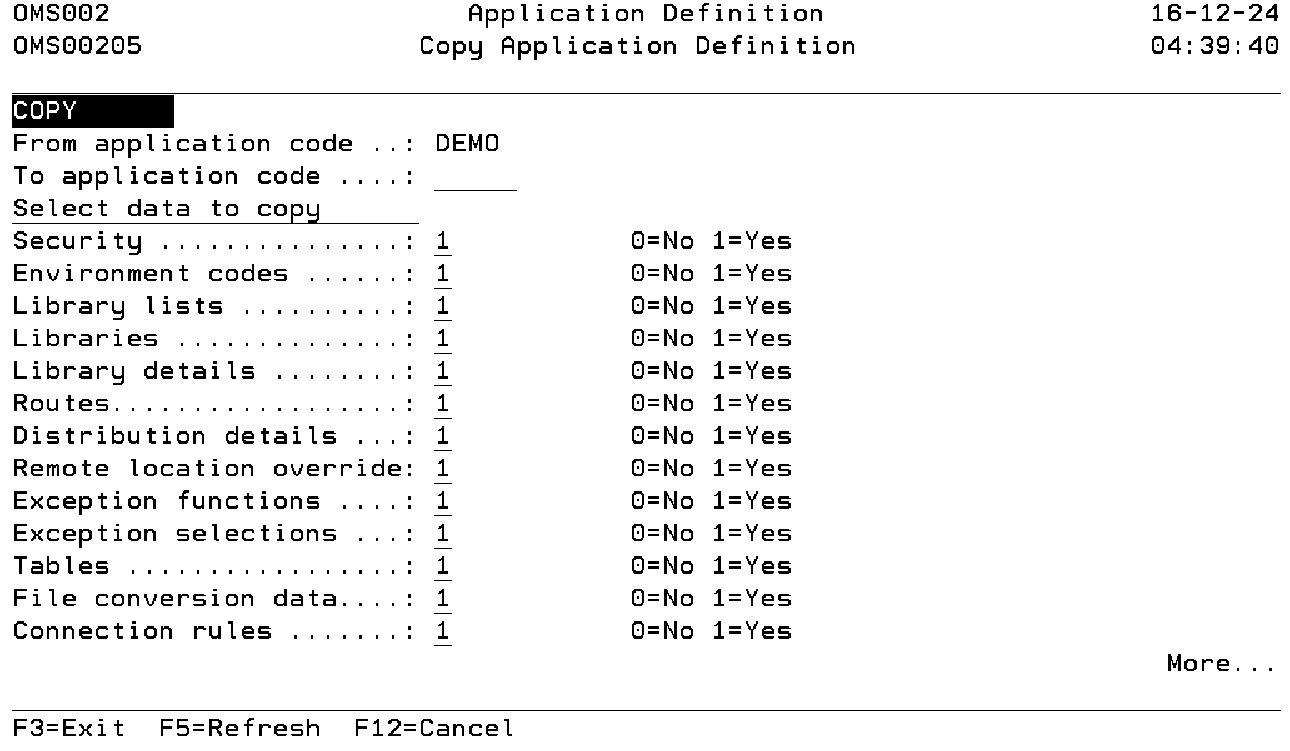
Copy Application Definition
The Copy Application definition function enables you to add an application definition using an existing application as a base for copying. The application attributes of the base application are always copied to the new application. Other descriptions can be selected to copy.
Copying of applications is useful if the extended descriptions of the new application has a lot in common with the application used as a base. You can also create a template application which will be used as a base for other applications.
Note: Don't forget to change the newly created application once it is copied.
Target application code
Use this prompt to enter the application code to be created. Refer to the description of Application code for a detailed description.
Security
Use this field to indicate that the user authority definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Environment codes.
Use this field to indicate that the environment definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Note: Copying of environments also include the security definitions per environment.
Library lists
Use this field to indicate that the library list definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Libraries
Use this field to indicate that the library definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Library details
Use this field to indicate that the library detail definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Routes
Use this field to indicate that the Route definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Distribution details
Use this field to indicate that the distribution list definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Remote location override
Use this field to indicate that the remote location override definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Exception functions
Use this field to indicate that the exception function definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Exception selections
Use this field to indicate that the exception selection definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Tables
Use this field to indicate that the table definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
File conversion data
Use this field to indicate that the file conversion definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Connection rules
Use this field to indicate that the application specific Connection rule definitions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
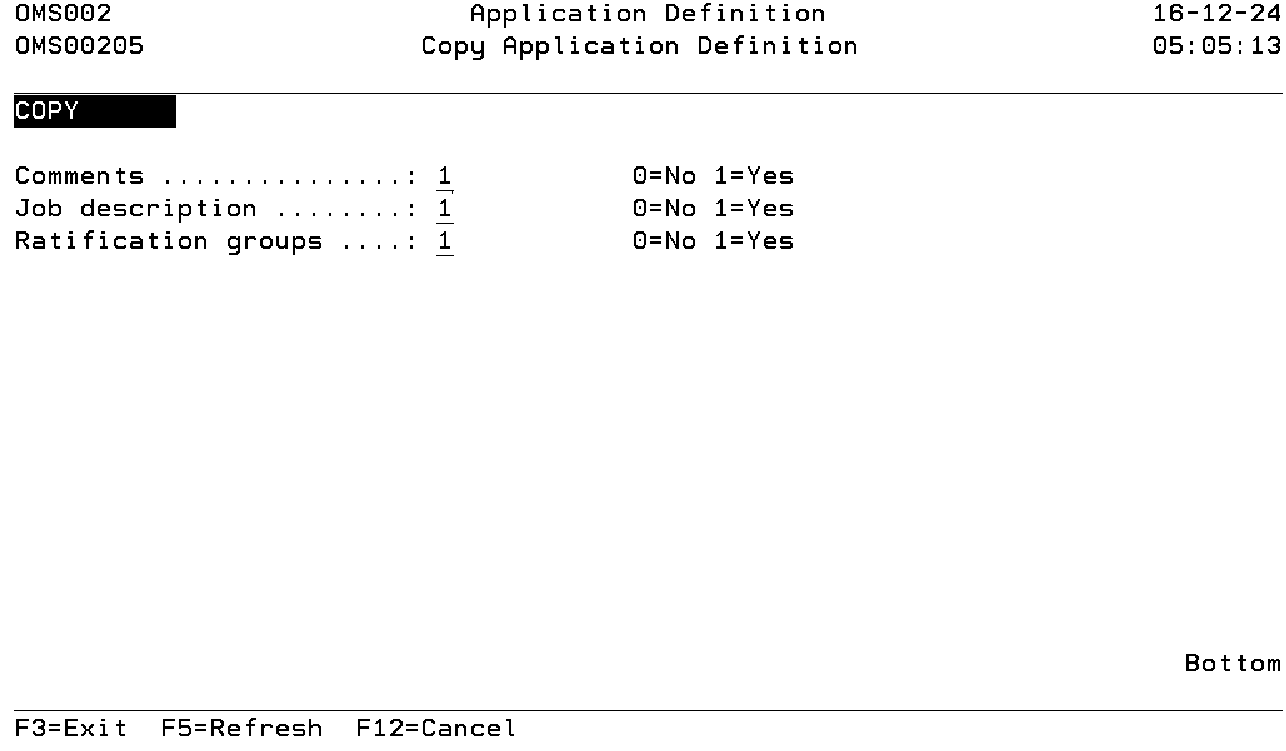
Comments
Use this field to indicate that the application specific comments have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Job description
Use this field to indicate if the job descriptions have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Ratification groups
Use this field to indicate if ratification groups have to be copied. Select value '1' to include these definitions. Select value '0' to exclude them.
Command Start Application Definition (STRAD)
This menu command starts the application definition function. Refer to the description of the function Application Definition for a detailed description.
STRAD
This command has no parameters.