UOA:TD/OMS User options
TD/OMS User options
The user option maintenance function allows you to create your own list options. The functions currently supported are the four major TD/OMS entities; Object Maintenance, Solution Maintenance, Request Maintenance and Fix Maintenance.
User options are available in the green screen and in the GUI.
The user options are cross application functions. This means that the user options are not owned by one of the applications, and all applications can use all user options.
A user option is always calling a user program or a user command. Commands can be executed on the client or on the server. You can specify if the program is to receive parameters. The parameters received are the data to the list entry on which the operation took place. TD/OMS comes with a few user options already installed. The sources of the corresponding programs reside in the QUSRSRC file in your TD/OMS library.
The user option program can be invoked by using the special user option '/' in the object maintenance, request maintenance, fix maintenance or solution maintenance displays. In the graphical user interface there is a special view to maintain user options.
User options can be made available for one user, or they can be assigned to just one user. If you are not an administrator then you can only remove, add and change a user option that is assigned to your user profile. You can ask the administrator to 'promote' a personal user option to a public user option.
You are able to override a public user option by a personal user option. A user option code and user code combination makes a user option unique.
Display 1 – Select User Option
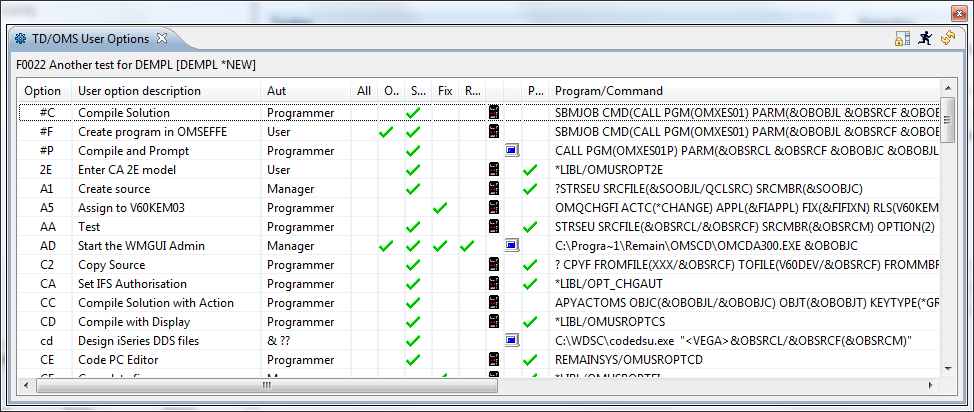
This display is the user option maintenance list. You can select an entry from the list to retrieve it into your program. If you are authorized, you are also able to maintain the user options by pressing the F8=Toggle Edit command key. Please note that user options are cross application. The user option you want to make, alter or remove can be used in other applications.
Press F11=View to show more columns with information.
Option
Use this column to perform different operations on individual objects. Type the option number next to an entry and press Enter. You can type the same option next to more than one entry at a time, and you can also type different options next to different entries at the same time.
Choose from the following:
- Select
- Type 1 to select the requested user option. After you pressed enter. The code will appear on the option line of the main function ;Display :Type 5 to display the user option.
User option
The user option is a user-defined code that can be used together with program defined options. User options normally operate on a list entry. The user option is associated with a user program that is activated when the user option is utilized. The user program performs the designated task and communicates the status of the operation to the calling program. See the technical description of the User Option Maintenance program for details.
User
This is the user for which the option is available. If you are not an administrator then you are able to create your own user options but you are not able to create user options for other people.
User option description
This is the description of the user option. It appears in the selection window and is used to identify the function of the user option.
Group
The group is the submenu in the graphical user interface context menu.
Program
If any, this is the program that is associated with the user option. You are also able to enter a command.
Library
If any, this is the library where the program resides.
Auth
This is the authorization level required to execute the user option. Authorization code \’0\’ indicates that the user option is disabled.
Check entry
This field indicates if TD/OMS should check if the user is authorized for the selected entry. This field should be set to *NO if the user option is not related to a particular entry. The user option CW (Command line in a window) is an example of such an option.
Parms
Indicates if parameters are passed. Only meaningful if the user option executes a program instead of a command.
All, Req, Fix, Sol, Obj
Indicates for which entity the user option is valid.
Display 1 – Work with user options
If you press F8=Toggle Edit the the display is the user option maintenance list. You can select an entry from the list to retrieve it into your program. If you are authorized, you are also able to maintain the user options. Please note that user options are cross application. The user option you want to make, alter or remove can be used in other applications. If you are not an administrator then you can only maintain your own user options.
Option
Use this column to perform different operations on individual objects. Type the option number next to an entry and press Enter. You can type the same option next to more than one entry at a time, and you can also type different options next to different entries at the same time.
Choose from the following:
- Select
- Type 1 to select the requested user option. After you pressed enter. The code will appear on the option line of the main function you used. After you pressed enter again the user option will be processed.
- Change
- Type 2 to change the attributes of the user option.
- Copy
- Type 3 to copy a user option to a new user option.
- Delete
- Type 4 to delete the user option.
- Display
- Type 5 to display the user option.
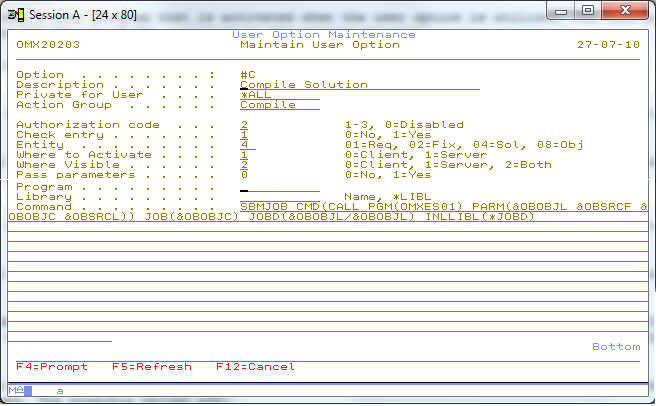
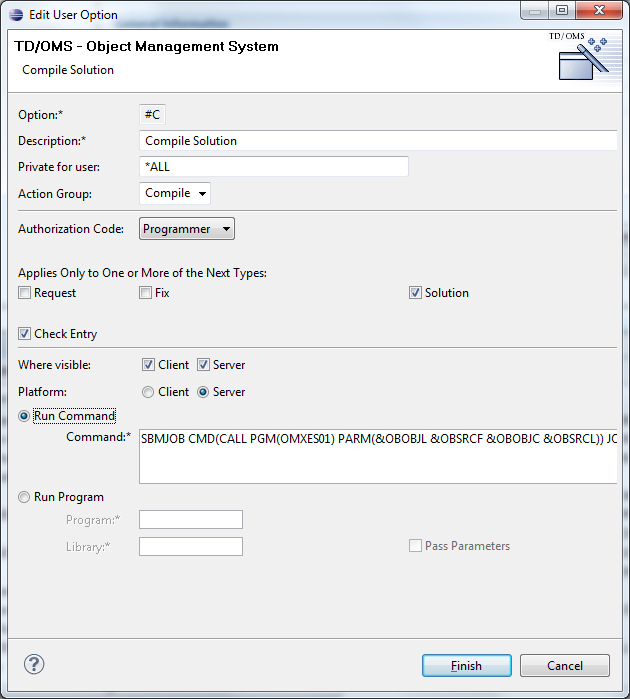
Display 2 – Maintain user option
This display is invoked by every list option except 4, Delete. The user options can be viewed, added, copied and changed in this display.
User option
The user option is a user-defined code that can be used together with program defined options. User options normally operate on a list entry.
The user option is associated with a user program that is activated when the user option is utilized. The user program performs the designated task and communicates the status of the operation to the calling program.
See the technical description of the User Option Maintenance program for details.
User option description
This is the description of the user option. It appears in the selection window and is used to identify the function of the user option.
Private for User
Enables you to define a user option for one specific person.
Action Group
The Action Group code can be used to group user options in logical groups. These groups will manifest themselves as submenus in the GUI.
Authorization
This is the authorization level required to execute the user option. Authorization code ‘0’ indicates that the user option is disabled.
Check entry
This field indicates if TD/OMS should check if the user is authorized for the selected entry. This field should be set to *NO if the user option is not related to a particular entry. The user option CW (Command line in a window) is an example of such an option. If set to *YES then e.g. programmers are not allowed to use the option against production objects.
Entity
This is a binary addition field. If the entity should be made available for requests and fix then the two values must be added (1+2=3). If the user option must be available for objects and solutions then the value should be 12 (4+8).
Where to activate
Defines where the user option must be activated. Please note that programs cannot be called on the client. These must be command strings that can be executed by the client operating system.
Where visible/Platform
Specifies where the entry is visible. Specify 0=Client to indicate that the user option is only valid in the graphical user interface, specify 1=Server to indicate that the user option is only visible in the green screen and use 2=both to make it visible everywhere.
Pass Parameters
This element specifies whether or not parameters are passed to the calling program. The possible values are:
0=No No parameters are passed to the calling program.
1=Yes Parameters are passed to the calling program.
Program and Library
- Library
- Contains the name of the library where the user option program can be found.
- Program
- Contains the name of the program that is called when the indicated user option is used. Please keep in mind that the program you are using may not adopt authority from the calling program. Otherwise, the program would adopt TD/OMS authority because all TD/OMS functions are owned by the user OMS (including the database).
Command
The Command String can be used to enter a command string that can be executed by TD/OMS. Depending on the entity code the attributes of the entity can be substituted. Please note that application fields are always available and object fields are available when a solution is processed (except when the solution is not yet registered in the components database.)
The values that can be substituted are:
Fields from Application Database
&APAPPL Application code
&APAPNM Application name
&APERPR Request manager
&APDMPL Dump library
&APGL4N 4-GL Name
&APSRCI Check source indicator
&APCRLS Release
&APCERR Request number
&APIERR Increment
&APCFIX Fix number
&APIFIX Increment
&APCNVS Data conversion scope
&APCATT Attribute conversion type
&APCATS Attribute conv. scope
&APCAUT Authorisation conv. type
&APCAUS Authorisation conv. scope
&APCJOT Journal conversion type
&APCJOS Journal conversion scope
&APMODC Module code
&APDRVC Derivation code
&APMTPC Message 2 programmer code
&APFBLC Fall back library
&APFJBD Fast JOBD
&APFJBL Fast JOBD library
&APSJBD Slow JOBD
&APSJBL Slow JOBD library
&APPATH Default Transfer Path
Fields from component database (objects)
&OBAPPL Application code
&OBENVC Environment code
&OBOBJC Object code
&OBOBJL Object library
&OBOBJT Object type
&OBOBJA Object attribute
&OBOBJD Object description
&OBSRCF Source file
&OBSRCL Source library
&OBSRCM Source member
&OBSRCS Sources belong to object
&OBSRCX Source Change date
&OBOBJX Object Source change date
&OBOMOD Object modified
&OBOCRT User which created object
&OBFIXN Fix number
&OBUSDF User defined
&OBEXCI May not exist indicator
&OBOCLS Object class
&OBVRSN Version number
&OBMODN Modification number
&OBCHGX Object Change date
&OBIOBC IFS object code
&OBIDRC IFS Directory code
&OBGLMC 4-GL Model code
&OBGLLC 4-GL Library code
&OBGLK2 4-GL Additional key 2
&OBGLK3 4-GL Additional key 3
&OBGLK4 4-GL Additional key 4
&OBGLK5 4-GL Additional key 5
&OBGL4N 4-GL Name
&OBGLMD 4-GL Model description
&OBROTC Route Code
&OBPTHX Path Extension code
&OBELBC Extended Library Code
&DTMBRC Member code
&DTMBRA Member attribute (MBSEU)
&DTMBRD Member text
&DTFIXN Fix number
&DTOMOD Object modified
&DTUSDF User defined
&DTEXCI May not exist indicator
&DTAPPL Application code
&DTVRSN Version number
&DTMODN Modification number
Fields from Solution database
&SOAPPL Application code
&SOFIXN Fix number
&SOOBJC Object code
&SOOBJT Object type
&SOOBJA Object attribute
&SOMBRC Member code
&SOOBJL Object library
&SOOCLS Object class
&SOENVC Environment code
&SOSRCP Source Processing
&SOVRSB Version number
&SOMODB Modification number
&SOVRSN Version number
&SOMODN Modification number
&SOOVRC Override code
&SOSOLT Solution type
&SOSTAT Status
&SOROTC Route Code
&SOELBC Extended Library Code
&SOPTHX Path Extension
Fields from Fix database
&FIAPPL Application code
&FIFIXN Fix number
&FIFIXT Fix type
&FIRLSN Release
&FIDEXN Development exit count
&FIREAC Reason code
&FIFIXS Fix status
&FIPRIN Priority numeric
&FIPGMR Programmer
&FIESDT Expected start date
&FIRSDT Realized start date
&FIECDT Expected completion date
&FIRCDT Realized completion date
&FIEDDT Expected dev. end date
&FIRDDT Realized dev. end date
&FIEPHN Expected number of hours
&FIERHN Realized number of hours
&FISHFD Short fix description
&FINACN Number of ratification grps
&FIACCN Ratification count
&FIREJI Rejected indicator
&FIFREE Free user space
&FIPATH Path code
Fields from Request database
&REAPPL Application code
&REREQN Request number
&REERRT Request type
&REENVC Environment code
&REREAC Reason code
&REPRIN Priority numeric
&REUSID User i.d., or user class
&READDR User address, distribution
&REUSRI Distributed user i.d.
&RETELN Telephone number
&REWCDT Requested completion date
&RERCDT Realized completion date
&REINDT Income date
&REINTM Income time
&RESHED Short request description
&RENACN Number of ratification grps
&REACCN Ratification count
&REREJI Rejected indicator
&REFREE Free user space
PDM
Besides these codes, the general PDM style substitutions can also be used where appropriate:
&A Object Attribute
&C User defined option code
&F Name of file containing selected member
&L Object or member library name
&N Name of selected resource
&O Object library
&S Item Type without *
&T Item Type
&X Object or member text in single quotes