Large data files management
TimeFlash is a TD/OMS interface for the third-party software MIMIX Promoter (SyncSort), also offered by Remain Software.
TimeFlash supports the change management of big data files in a live (production) environment. The TimeFlash interface streamlines and speeds up the software change process significantly while decreasing downtime caused by updating data files and reduces the amount of time needed for deployment.
TimeFlash makes data content copying and the final replacement of a file as fully separated processes: All actual data of the file is copied to a separate duplicate of a newer version of the file, and all changes to the file are updated into the duplicate. As soon as the file in process becomes available, the original one is set apart and the duplicate will be transferred to the active location.
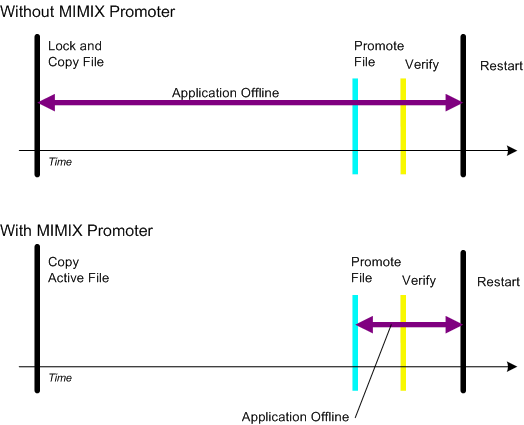
Benefits of big data files management with TimeFlash and MIMIX Promoter
- Streamlined and faster software change process.
- Decreased downtime.
- Reduced time spent on deployment.
- Data content copying and and the final replacement as fully separated processes.
- Software availability 24/7.
- Increased employee productivity.
The majority of the TimeFlash-specific process definitions are performed during the Object Transfer process. The interface module consists of a series of exception functions, which can be implemented as Exception or Action procedures to support a vast amount of implementation strategies. The TD/OMS TimeFlash menu enables access to the TimeFlash interface functions outside of the TD/OMS transfer process.
The Apply TimeFlash copy in TD/OMS transfer command is commonly used to start a data copy of a file in active use as part of an object transfer process.

